10 Surprising Facts About the Silk Road in China
Travellers along the Silk Road in China were attracted not only by trade but also by the intellectual and cultural exchange taking place in cities along the Silk Road, many of which developed into hubs of culture and learning. Today, we would like to share with you the 10 most commonly asked questions about the silk road.
Ready to uncover the lesser-known side of this iconic route? We hope all these interesting facts will broaden your horizon and help you gain more knowledge before your Silk Road adventure.
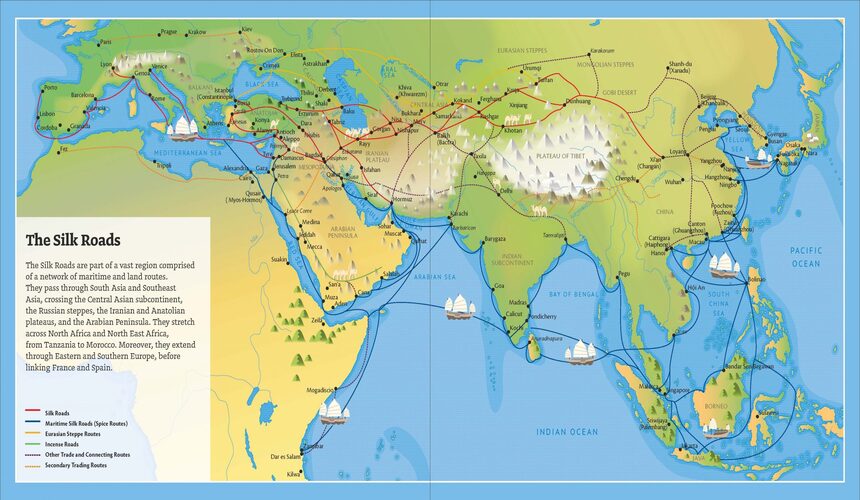
Resource: https://en.unesco.org/silkroad/about-silk-roads
1. Why do we name it the Silk Road?
The name, silk road comes from the most popular Chinese goods – silk. It was officially named after the German geographer and traveler Ferdinand Von Richthofen first used the term “silk road” in 1877 C.E. to describe the trade pathways between Europe and East Asia. His student, the renowned Swedish geographer, and explorer Sven Hedin, published a book entitled “The Silk Road” in 1934.
2. What is the Silk Road?
The Silk Road generally refers to the Land Silk Road, which is broadly divided into Land Silk Road and Maritime Silk Road. In 1877, the German geographer Ferdinand Von Richthofen defined “the western region traffic road mediated by silk trade between China and Central Asia as well as India” as “the Silk Road”.
3. Who started the Silk Road?
In China’s history, the first person to pass the route was Zhang Qian, an envoy sent by Emperor Wu in Han Dynasty (142 BC). But unfortunately, he was twice imprisoned by the Xiongnu army. After 13 years, he finally returned to Chang’an and made his reports from his journey conveying valuable information about the people and lands that lay to the West. After his visits, the emissaries of various countries such as Persia also came to visit Chang’an, and many foreign businessmen came to China for trade.
4. How long was the Silk Road?
The silk road often refers to the land Silk Road that extended approximately 6,437 kilometers (4,000 miles) across some of the world’s most formidable landscapes, such as the Gobi Desert and the Pamir Mountains. As for the Maritime Silk Road, it was over 15,000 kilometers (9375miles) in length, as it stretched from the west coast of Japan to the Mediterranean of Europe.
5. Where is the Silk Road?
Land silk road was a vast network of trade routes that spanned the entire continent of Asia from China’s Chang’an, connecting parts of north Africa and the Mediterranean sea area. Apart from the land transportation, there was also another route which was the Maritime Silk Road. It spreads outward from the South China Sea, with several branches connecting North Korea, Japan, Ryukyu, and other countries.
6. How long did it take to cross the Silk Road in ancient times?
The monk Xuanzang spent about 17 years on the road to get from Chang’An (now Xi’an) to India. It is said that he traveled from the Gansu corridor to Dunhuang, across the Tarim Basin, to Kashgar, and across the mountains to Samarkand, so he might had to walk 2300 miles. This distance could be completed in about 200 days for a man walking without ceasing at night.
7. When did the Silk Road begin and end?
It is believed that the silk road started from the Han Dynasty (130 B.C). But before that, the trade activities might had begun a long time ago. It had been used for nearly 600 years and had a great impact on international trade and cultural exchanges until the Ottoman Empire closed the trade routes.8. Where did the Silk Road start and end?
8. Where did the Silk Road start and end?
It’s believed that the Silk Road started from Chang’an City (today’s Xi’an), and later from Luoyang during the East Han Dynasty and stretched westward to reach the Roman Empire.
9. Was paper spread through the Silk Road?
China’s invention of paper didn’t stay within its borders for long. Through the Silk Road, it traveled westward. Revolutionized education, record-keeping, and communication in other parts of the world.
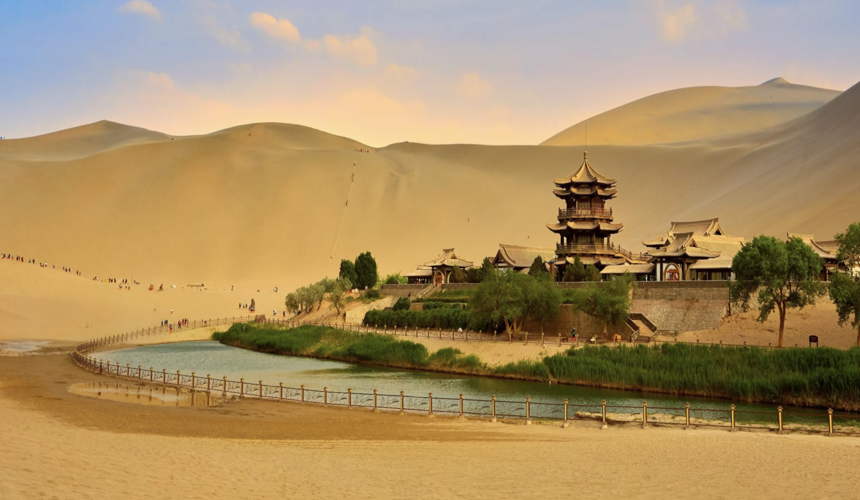
10. You can still follow the route today
Many sections of the Silk Road in China are open to modern travelers. Whether you’re exploring ancient ruins, hiking through deserts, or savoring Uyghur cuisine in Xinjiang. The journey offers a rare blend of adventure and history.
The Silk Road is more than just a path through time. It’s a journey through cultures, landscapes, and ideas that continue to influence the world today. Whether you’re a history buff, a cultural explorer, or an intrepid traveler. China’s Silk Road promises discoveries at every turn.
So pack your bags, lace up your boots, and let the ancient road lead you on a journey you’ll never forget. Book your custom tour now. Chat with our travel consultant to start planning your unforgettable adventure. Let us help you turn history into a hands-on experience!




